In Q1 2022, the sales volume of semiconductor equipment in South Korea was US $5.15 billion, ranking second in the world From Semiconductor industry observation
The following is the In Q1 2022, the sales volume of semiconductor equipment in South Korea was US $5.15 billion, ranking second in the world From Semiconductor industry observation recommended by recordtrend.com. And this article belongs to the classification: Hardware equipment industry, High end equipment manufacturing industry.
“Science and technology are the most important thing in our country”. In recent years, under the influence of epidemic and geopolitical factors, more and more countries and regions began to realize the importance of semiconductors. Even the United States officially passed the “chip and Science Act” on July 28. In addition, Japan, China, India, Malaysia, Vietnam and other Asian countries have also increased the layout of the chip industry, including, of course, the storage power – South Korea.
It is well known that Samsung and SK Hynix, the two leading storage companies, have shouldered the semiconductor industry in South Korea. They also know that South Korea’s semiconductor is weak in the field of equipment and materials, but they do not know how the semiconductor equipment industry in South Korea is developing today? In this article, the author will review the development of semiconductor equipment industry in South Korea and the equipment manufacturers they own.
From 18% to 20%, the development history of Korean equipment
Equipment and materials have always been the pain and weakness of the Korean semiconductor industry. The professor of materials science and engineering at the University of Incheon, South Korea, once published an article entitled “current situation and analysis of the domestic semiconductor materials and equipment industry”. He believed that the biggest reason for the difficulty in the development of materials and equipment in South Korea was the lack of talents and experience.
Unlike other fields, the material and equipment industry is more technology intensive and highly integrated. At present, major equipment countries such as the United States and Japan have passed the initial stage of the so-called “complete set” industry (assembly of televisions and washing machines, etc.). Due to their late development, China, Vietnam, South Korea and other countries will not be able to fully cultivate professional labor with a variety of knowledge and experience in physics, chemistry, chemical engineering, materials, electronics and so on, Otherwise, it will be difficult to develop.
Another reason is that the structural problems of South Korea’s semiconductor industry are highly concentrated in memory, but isolated from other countries. A person in charge of a semiconductor equipment manufacturer who asked not to be named said, “it should be said that except for Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix partners, there is almost no place to make profits. This has also hindered the development of the semiconductor equipment industry in South Korea to a certain extent.
The difficulty in the development of South Korea’s equipment industry is reflected incisively and vividly in terms of localization rate. In 2006, a paper on the medium and long term development strategy of Korean semiconductor equipment and raw material industry mentioned that the localization rate of Korean semiconductor equipment remained at the line of 18% based on 2004. According to the semiconductor equipment technology training center, the localization rate of semiconductor equipment in South Korea was still 20% in 2021, and the technology in the cleaning field (materials, parts, equipment) was relatively weak. This means that after nearly 20 years of development, the localization rate of semiconductor equipment in South Korea has only increased by 2%. It can be seen that the development of the equipment field is difficult.
The “fuse” to stimulate South Korea to develop semiconductor equipment is the “semiconductor dispute between Japan and South Korea” in 2019. Japan, a powerful equipment country, has seized the throat of semiconductor development, making South Korea aware of the importance of equipment localization. According to the report of Korean media JoongAng in 2018, the localization rate of Korean semiconductor equipment industry is only 18.2%. Compared with the above data, it is not difficult to find that Korean semiconductor equipment industry finally began to make new progress after the semiconductor dispute between Japan and South Korea in 2019.
The most intuitive is the policy support. In August 2019, the Korean government announced the “measures to strengthen the competitiveness of materials, parts and equipment” to get rid of the external industrial structure. This measure includes measures to inject national resources and capabilities, such as budget, finance, taxation, location and special regulations, to address the structural weaknesses of the domestic materials, parts and equipment industry. In addition, the measures also include a number of supporting policies, but the most important thing is to support the establishment of a strong cooperation model between supply and demand enterprises and demand enterprises, so as to enhance the overall competitiveness of the materials, parts and equipment industry.
Just recently, the South Korean government said that it would invest 340trillion won (259billion US dollars) in the chip industry to pave the way in the next five years, train more than 150000 skilled workers in this field, and plan to realize the localization of 50% of the key materials, components and equipment in the chip industry by 2030.
According to semi data last year, South Korea is expected to invest $30billion (35.106 trillion won) in semiconductor wafer plant equipment this year, becoming the world’s largest country by country investment.
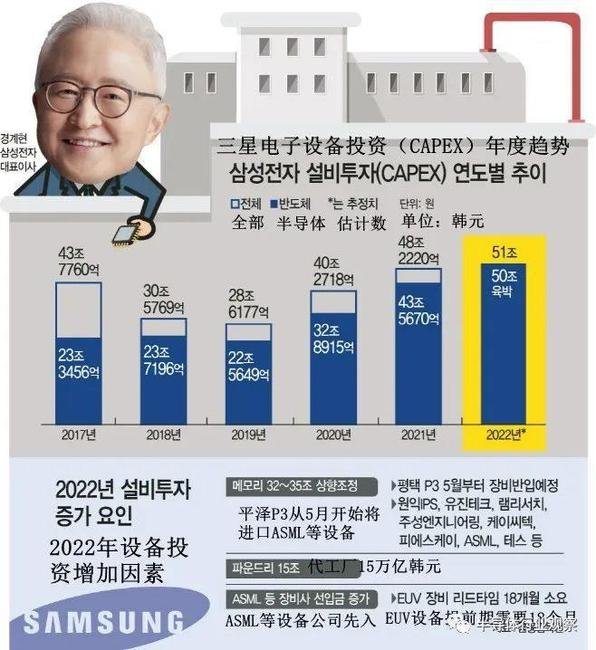
Corresponding to the policy is the substantial investment of enterprises. According to South Korean media asiatoday, the facility investment of the semiconductor business led by the president of Samsung electronics GUI Jingxuan is expected to reach 50 trillion won this year, while its semiconductor facility investment last year exceeded 43 trillion won.
Annual trend of Samsung electronic equipment investment
Source: asiatoday
In addition, according to the business report submitted by Samsung Electronics and the invested enterprises to the Korea Stock Exchange last September, from July 2020 to September 2021, Samsung Electronics has invested in at least eight Korean listed enterprises and the subsidiaries of one listed enterprise, a total of nine, including semiconductor testing equipment manufacturer Yik Corporation, wafer grinding equipment manufacturer KC tech Lot vacuum, a manufacturer of vacuum pump equipment, and new power plasma, a manufacturer of wafer cleaning related equipment.
At the same time, SK Hynix also maintained a conservative investment position. In 2018, it invested 17.38 trillion won in semiconductor facilities, reduced to 12.747 trillion won in 2019, reduced to 9.89 trillion won in 2020, and increased to 13.4 trillion won in 2021. According to kiwoom securities, SK Hynix’s facility investment this year is expected to increase by 47% over the previous year, reaching 17 trillion won.
According to the Korean economic news network, SK Group decided to invest 29billion dollars in the United States in four major fields, including semiconductors, electric vehicle batteries, green energy and biotechnology. Among them, US $15billion will be used in the semiconductor field. SK Hynix, a semiconductor subsidiary of SK group, plans to build cutting-edge packaging and manufacturing equipment and research and development (r&d) centers for memory semiconductors in the United States.
Emerging Korean semiconductor equipment manufacturers
After three years of research and development and investment, the sales of Korean equipment ranked second in the world with us $5.15 billion (about 6.445.2 billion won) in the first quarter of this year.
In terms of the development of semiconductor equipment process, at present, in terms of front-end equipment, the technology of Korean equipment manufacturers is at the level of 60-80% of the etching, cleaning and deposition process at the core of production. The heat treatment equipment used for deposition process is competitive in the global market, but the technical foundation of exposure equipment, ion implantation equipment and measurement and analysis equipment is weak. In the field of downstream equipment, Korean equipment manufacturers are generally at a competitive level. According to the Korea Industrial Technology Evaluation and Planning Institute, this is because Korean companies have focused on processes with relatively low entry barriers due to the technology gap and the burden of investment costs.
This can be seen from the list of Korean semiconductor front-end equipment suppliers compiled by semiconductor comprehensive research recently, as well as the technical level and localization rate of Korean semiconductor materials of Korean industrial technology evaluation and Planning Institute.
List of Korean semiconductor front channel equipment suppliers
Figure source: semiconductor comprehensive research
Equipment manufacturers by major semiconductor process, domestic technical level and localization rate (unit:%)
Korean Institute of industrial technology evaluation and planning
Drawing: semiconductor industry observation
It can be seen from the above two figures that Korean semiconductor front-end equipment manufacturers are mainly concentrated in the field of deposition and heat treatment. Compared with lithography exposure, ion implantation, measurement and analysis equipment, the localization rate of deposition, heat treatment and flattening equipment is higher.
In the semiconductor mania of 2021, South Korean equipment manufacturers also made great achievements. According to the analysis of the second quarter performance of 31 domestic semiconductor equipment companies by Korean media the elec last August, the number of equipment manufacturers with quarterly sales of more than 100billion won increased from 5 in 2020 to 9 in 2021, including semes, wonik IPS, SFA, KC, AP systems, PSK, EO technologies, Hanmi semiconductor and tes. The five companies with sales growth of more than three digits are Yik, new power plasma, jusung engineering, Intek plus and exicon. Here the author briefly introduces several Korean equipment manufacturers:
Semes, founded in 1993, is a semiconductor equipment supplier under Samsung Electronics and the largest equipment manufacturer in South Korea. It produces core semiconductor and display equipment and has entered the top 10 of the world’s equipment industry for six consecutive years. Its goal is to achieve sales of 5trillion won by 2030 and enter the top 5 of the world. At present, semes’ products mainly include cleaning (lotus, blueice prime), phototrack (omega-s, omega-k), etching (michelan O3, michelan C4) equipment in the field of semiconductor previous process, as well as bonder, probe, test handler and other equipment in the field of subsequent process.
Semes, a chip manufacturing equipment subsidiary of Samsung Electronics, said on Friday that its revenue in 2021 was KRW 3.12 trillion and its operating profit was KRW 353.3 billion, theelec reported. Businesskorea reported last April that semes is planning to build a new R & D center to help Samsung achieve independence in the field of semiconductor equipment.
Wonik IPS, founded in 1991, mainly provides plasma chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) equipment. In October 2020, wonik IPS mass produced the new metal CVD equipment “NOA” for the first time and supplied it to sk Hynix Qingzhou M15. This mass production of wonik IPS realized the localization of metal CVD equipment that had never been commercialized in the Korean equipment industry before. In September 2021, wonik IPS dry etching equipment for QD display was approved by Samsung display.
PSK is a semiconductor equipment company, mainly producing photoresist removal equipment (prstrip) and oxide film removal equipment (dry cleaning) for semiconductor etching process. In the category of semiconductor equipment, PSK is mainly applicable to wafer fabric equipment: dry strip, dry cleaning, new hard mask strip, wafer edge clean, etch back, power device etch. It has always maintained the world’s first market share in the plasma dry strip (photoresist stripping system) of semiconductor manufacturing process.
Late last year, PSK completed the development of “bevel etcher”. Since 2020, PSK has supplied strip equipment for the system semiconductor process of American semiconductor company. CEO Lee said, “in the semiconductor field, we plan to expand our business from memory to system semiconductor and expand our equipment portfolio from stripping equipment to cleaning and etching equipment.
In addition, as early as 2017, jusung engineering developed atomic layer deposition equipment (ALD) and provided it to system semiconductor manufacturers. In 2021, the sales volume was 377.2 billion won, an increase of 218.3% year-on-year.; TES is a company that manufactures semiconductor manufacturing equipment. It produces pretreatment core equipment for manufacturing chips by processing wafers in the semiconductor process. Its main customers are Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix. It is expected to enter the OEM of gas etching equipment and provide DRAM with new thin-film PECVD equipment.
In the field of back channel equipment, besides semes, Hanmi is also a large back channel equipment manufacturer. Founded in 1980, Hanmi ranks first in the “visual mounting equipment” market, cutting and inspecting wafers in the post process, and focuses on “EMI shielding equipment”. In the second quarter of last year, Hanmi successfully realized the localization of EMI shielding equipment “micro saw equipment”, obtained customers such as Samsung motor, chip packaging technology, UTAC, and put into production for the first time.
In addition, EO technologies, founded in 1989, is mainly engaged in the development and production of lasers and equipment for semiconductor, display and PCB manufacturing engineering; Intek plus, a manufacturer of visual inspection equipment for semiconductor back-end processes, won equipment orders from new Japanese customers such as Kyocera and ibedon in 2020. When the new factory in Daejeon is put into operation this year, the equipment capacity is expected to double; Genesem, a post-processing equipment manufacturer, developed EMI shielding equipment in 2016. It is understood that the new equipment 16 parallel non memory test processor was also supplied to South Korea OSAT company in the second quarter of last year.
The four major equipment manufacturers in the world have accelerated their entry
In addition to the rise of local equipment manufacturers, in recent years, global semiconductor equipment manufacturers such as Amat, ASML, Lam research, and Tokyo electronics have also accelerated their move to South Korea. Korean media analyzed the reasons, mainly in the following two aspects:
First, equipment manufacturers are aware of the importance of strengthening cooperation with major semiconductor manufacturers. The epidemic in 2020 made people feel the variability of the pattern and the importance of “binding”. Automobile manufacturers began to bind with chip enterprises, and chip enterprises began to bind with wafer foundries. It seems that only “binding” can bring them a sense of security in this turbulent situation.
More importantly, the storage semiconductor industry itself is a highly equipment dependent field. 70% of the investment of the memory semiconductor factory is used for equipment. However, more than 60% of the equipment installed on the production lines of Korean semiconductor manufacturers such as Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix depend on imports. This means that if you spend 30 trillion won to build a factory, you will spend 21 trillion won to buy equipment, of which nearly 13 trillion won is earned by foreign companies. For equipment manufacturers, South Korea, a storage power, has naturally become a big country that needs to maintain cooperative relations.
Second, equipment manufacturers generally believe that Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix will not change their leading positions in the global storage semiconductor market. South Korea is a well deserved large storage country, accounting for nearly 70% of the global memory semiconductor market share. Even if the overall storage market is in a downward cycle, Samsung and SK Hynix, as the leading storage enterprises, have technology leadership and strong pricing ability. Therefore, they have stronger anti risk ability than small and medium-sized enterprises, and can meet the next wave of upsurge in the storage industry. This can also be seen from the financial reports of Samsung and SK Hynix. Even though the storage is in the downward cycle, the financial reports of the two companies in the second quarter still set a new record.
In addition, South Korea is also catching up in the field of wafer foundry, and currently ranks second in the world with an 18% share in the wafer foundry market.
The above two points can also be well reflected in the site selection of the four major equipment manufacturers.
Applied materials company (Amat), the world’s largest semiconductor equipment manufacturer, officially announced on July 6 that it would jointly set up a research and development (r&d) center in South Korea with the Ministry of industry, trade and resources of South Korea and Gyeonggi do. The specific location, scale and timing of investment attraction have not been determined, but it is expected to build a high-tech R & D center in Gyeonggi do, which has semiconductor centers such as Longren, pingze, Huacheng, Lichuan, etc. According to Korean media ddaily, applied Korea CEO Mark Lee stressed: “we have established a research and development center in South Korea to strengthen our technology leadership and support the future development of the semiconductor industry.” It is reported that after the new R & D center is put into operation, it is expected to easily produce customized products for Korean semiconductor enterprises.
Source: ddaily
Lam research opened a South Korean technology center in Gyeonggi do in Longren city in April this year, which was built at the level of American and European research institutions and is responsible for the development of the most advanced equipment. Lam research established Lam research manufacturing Korea production Corporation in 2011 and began to localize major parts suppliers to Korean companies in 2003. In 2018, the forestry research technology training center was established. Lam research manufacturing Korea operates Huacheng factory after Wushan and Longren, doubling its equipment production capacity in South Korea. In February this year, Lam research also announced that it would produce high selective precision etching equipment for the next generation transistor structure gate ring (GAA) process in South Korea.
Tokyo Electronics (TEL) established the pyeonggi technology support center in pyeonggi in 2020, and plans to invest 100billion won from April this year to expand the R & D facilities of Huacheng on a large scale.
ASML also started a comprehensive Korean investment. In November 2021, it announced that it would invest 240 billion won in Gyeonggi province by 2024 to build a high-tech semiconductor cluster. In April this year, ASML CEO Peter wennink also visited South Korea. According to Yonhap, South Korea Gyeonggi do Huacheng quoted wennink as saying, “ASML Huacheng semiconductor cluster is progressing smoothly”.
Combined with the site selection of the four major semiconductor manufacturers, it can be seen that they are basically located in Huacheng, Gyeonggi Province, close to the semiconductor production facilities of Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix. Therefore, it is expected to shorten the cooperation distance, shorten the time of equipment and technology development, and maximize efficiency.
With the global materials and equipment companies establishing bases in Korea, even in the case of unpredictable risks such as global logistics difficulties, Korean semiconductor manufacturers are expected to avoid a fatal blow to the supply and demand of materials and equipment, thereby promoting the stability of the supply chain. Especially at the moment of equipment shortage, the delayed delivery of core semiconductor equipment has also affected the plant expansion plans of Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix to a certain extent. Trendforce has said that (due to the delayed delivery of equipment), the semiconductor expansion plan will be postponed for about 2 to 9 months.
It has to be said that whether for South Korea or China, the development of the semiconductor equipment industry is doomed to be blocked and long, but as a key part of the semiconductor industry chain, it should not be given up easily anyway. More importantly, the current era of Fabs blooming everywhere may bring more opportunities and challenges to semiconductor equipment manufacturers.
More reading from semiconductor industry observation: Korean customs office: the total value of Korean semiconductor exports in 2017 reached US $99.71 billion IC insights: microprocessor sales will increase by 12% in 2022 to reach a record US $114.8 billion semiconductor industry observation: q2sk Hynix’s annual revenue will increase by 56% to 4.2 trillion won in 2022, and the chip industry is in two hot and cold days etnews: ASML will expand the sales target of Korea in 2025 to 14.75 billion euros SK Hynix financial report: 2020 In Q1, SK Hynix’s net profit was 3.7 billion yuan, a year-on-year decrease of 41% trendforce: in 2022, Q1’s enterprise SSD revenue reached 5.58 billion US dollars, with a month on month increase of 14.1% trendforce: in 2021, the output value of the top ten wafer manufacturers in Q4 reached 29.55 billion US dollars, hitting a new high for ten consecutive quarters Samsung: 4q19 degree net profit of 4.4 billion US dollars, a year-on-year decrease of 38.2% counterpoint research: in 2022, Samsung’s revenue share in the global smart phone chipset market was only 7% knometa: in 2021, the global wafer market Top 5 enterprises in total production capacity account for 56%. Samsung ranks first in counterpoint: it is expected that the CIS market will reach US $21.9 billion in 2022, and Samsung will further narrow the gap with Sony. DisplaySearch: in 2013, the global large LCD panel shipments will reach 698million. Korean manufacturers account for half. Omdia: in 2022, Samsung Electronics World TV market sales accounted for 29.5%, ranking first in market share for 16 consecutive years. Samsung: by the end of November 2021, the frame TV sales have reached 1million Taiwan theelec: semes, a subsidiary of Samsung, made a full year operating profit of 353.3 billion won in 2021, the best annual performance so far
If you want to get the full report, you can contact us by leaving us the comment. If you think the information here might be helpful to others, please actively share it. If you want others to see your attitude towards this report, please actively comment and discuss it. Please stay tuned to us, we will keep updating as much as possible to record future development trends.
RecordTrend.com is a website that focuses on future technologies, markets and user trends. We are responsible for collecting the latest research data, authority data, industry research and analysis reports. We are committed to becoming a data and report sharing platform for professionals and decision makers. We look forward to working with you to record the development trends of today’s economy, technology, industrial chain and business model.Welcome to follow, comment and bookmark us, and hope to share the future with you, and look forward to your success with our help.




